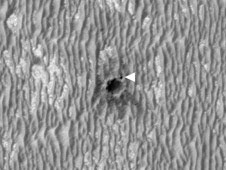
Weird coatings on rocks beside a young Martian crater remain puzzling after a preliminary look at data from examination of the site by NASA's Opportunity rover.
The rover spent six weeks investigating the crater called "Concepción" before resuming its long journey this month. The crater is about 10 meters (33 feet) in diameter. Dark rays extending from it, as seen from orbit, flagged it in advance as a target of interest because the rays suggest the crater is young.
The rocks ejected outward from the impact that dug Concepción are chunks of the same type of bedrock Opportunity has seen at hundreds of locations since landing in January 2004: soft, sulfate-rich sandstone holding harder peppercorn-size dark spheres like berries in a muffin. The little spheres, rich in iron, gained the nickname "blueberries."
 "It was clear from the images that Opportunity took on the approach to Concepción that there was strange stuff on lots of the rocks near the crater," said Steve Squyres of Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y., principal investigator for Opportunity and its twin rover, Spirit. "There's dark, grayish material coating faces of the rocks and filling fractures in them. At least part of it is composed of blueberries jammed together as close as you could pack them. We've never seen anything like this before."
"It was clear from the images that Opportunity took on the approach to Concepción that there was strange stuff on lots of the rocks near the crater," said Steve Squyres of Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y., principal investigator for Opportunity and its twin rover, Spirit. "There's dark, grayish material coating faces of the rocks and filling fractures in them. At least part of it is composed of blueberries jammed together as close as you could pack them. We've never seen anything like this before."Opportunity used tools on its robotic arm to examine this unusual material on a rock called "Chocolate Hills." In some places, the layer of closely packed spheres lies between thinner, smoother layers. "It looks like a blueberry sandwich," said Matt Golombek, a rover science-team member at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
Initial analysis of the coating's composition does not show any obvious component from whatever space rock hit Mars to dig the crater, but that is not a surprise, Golombek said. "The impact is so fast, most of the impactor vaporizes," he said. "Thin films of melt get thrown out, but typically the composition of the melt is the stuff that the impactor hit, rather than the impactor material."
The composition Opportunity found for the dark coating material fits at least two hypotheses being evaluated, and possibly others. One is that the material resulted from partial melting of blueberry-containing sandstone from the energy of the impact. Another is that it formed from filling of fractures in this type of rock before the impact occurred.
No comments:
Post a Comment