The highest-resolution-yet temperature map and images of Saturn's icy moon Mimas obtained by NASA's Cassini spacecraft reveal surprising patterns on the surface of the small moon, including unexpected hot regions that resemble "Pac-Man" eating a dot, and striking bands of light and dark in crater walls.
"Other moons usually grab the spotlight, but it turns out Mimas is more bizarre than we thought it was," said Linda Spilker, Cassini project scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. "It has certainly given us some new puzzles."

Cassini collected the data on Feb. 13, during its closest flyby of the moon, which is marked by an enormous scar called Herschel Crater and resembles the Death Star from "Star Wars."
Scientists working with the composite infrared spectrometer, which mapped Mimas' temperatures, expected smoothly varying temperatures peaking in the early afternoon near the equator. Instead, the warmest region was in the morning, along one edge of the moon's disk, making a sharply defined Pac-Man shape, with temperatures around 92 Kelvin (minus 294 degrees Fahrenheit). The rest of the moon was much colder, around 77 Kelvin (minus 320 degrees Fahrenheit). A smaller warm spot - the dot in Pac-Man's mouth - showed up around Herschel, with a temperature around 84 Kelvin (minus 310 degrees Fahrenheit).
The warm spot around Herschel makes sense because tall crater walls (about 5 kilometers, or 3 miles, high) can trap heat inside the crater. But scientists were completely baffled by the sharp, V-shaped pattern.
"We suspect the temperatures are revealing differences in texture on the surface," said John Spencer, a Cassini composite infrared spectrometer team member based at Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colo. "It's maybe something like the difference between old, dense snow and freshly fallen powder."
Denser ice quickly conducts the heat of the sun away from the surface, keeping it cold during the day. Powdery ice is more insulating and traps the sun's heat at the surface, so the surface warms up.
Even if surface texture variations are to blame, scientists are still trying to figure out why there are such sharp boundaries between the regions, Spencer said. It is possible that the impact that created Herschel Crater melted surface ice and spread water across the moon. That liquid may have flash-frozen into a hard surface. But it is hard to understand why this dense top layer would remain intact when meteorites and other space debris should have pulverized it by now, Spencer said.
"Other moons usually grab the spotlight, but it turns out Mimas is more bizarre than we thought it was," said Linda Spilker, Cassini project scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. "It has certainly given us some new puzzles."

Cassini collected the data on Feb. 13, during its closest flyby of the moon, which is marked by an enormous scar called Herschel Crater and resembles the Death Star from "Star Wars."
Scientists working with the composite infrared spectrometer, which mapped Mimas' temperatures, expected smoothly varying temperatures peaking in the early afternoon near the equator. Instead, the warmest region was in the morning, along one edge of the moon's disk, making a sharply defined Pac-Man shape, with temperatures around 92 Kelvin (minus 294 degrees Fahrenheit). The rest of the moon was much colder, around 77 Kelvin (minus 320 degrees Fahrenheit). A smaller warm spot - the dot in Pac-Man's mouth - showed up around Herschel, with a temperature around 84 Kelvin (minus 310 degrees Fahrenheit).
The warm spot around Herschel makes sense because tall crater walls (about 5 kilometers, or 3 miles, high) can trap heat inside the crater. But scientists were completely baffled by the sharp, V-shaped pattern.
"We suspect the temperatures are revealing differences in texture on the surface," said John Spencer, a Cassini composite infrared spectrometer team member based at Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colo. "It's maybe something like the difference between old, dense snow and freshly fallen powder."
Denser ice quickly conducts the heat of the sun away from the surface, keeping it cold during the day. Powdery ice is more insulating and traps the sun's heat at the surface, so the surface warms up.
Even if surface texture variations are to blame, scientists are still trying to figure out why there are such sharp boundaries between the regions, Spencer said. It is possible that the impact that created Herschel Crater melted surface ice and spread water across the moon. That liquid may have flash-frozen into a hard surface. But it is hard to understand why this dense top layer would remain intact when meteorites and other space debris should have pulverized it by now, Spencer said.
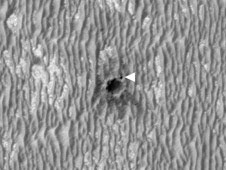
 "It was clear from the images that Opportunity took on the approach to Concepción that there was strange stuff on lots of the rocks near the crater," said Steve Squyres of Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y., principal investigator for Opportunity and its twin rover, Spirit. "There's dark, grayish material coating faces of the rocks and filling fractures in them. At least part of it is composed of blueberries jammed together as close as you could pack them. We've never seen anything like this before."
"It was clear from the images that Opportunity took on the approach to Concepción that there was strange stuff on lots of the rocks near the crater," said Steve Squyres of Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y., principal investigator for Opportunity and its twin rover, Spirit. "There's dark, grayish material coating faces of the rocks and filling fractures in them. At least part of it is composed of blueberries jammed together as close as you could pack them. We've never seen anything like this before."





 Cassini's closest-ever flyby of Saturn's
Cassini's closest-ever flyby of Saturn's 

 Flowing lava can carve or build paths very much like the riverbeds and canyons etched by water, and this probably explains at least one of the meandering channels on the surface of Mars. These results were presented on March 4, 2010 at the 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference by Jacob Bleacher at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. Whether channels on
Flowing lava can carve or build paths very much like the riverbeds and canyons etched by water, and this probably explains at least one of the meandering channels on the surface of Mars. These results were presented on March 4, 2010 at the 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference by Jacob Bleacher at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. Whether channels on  Bleacher and his colleagues carried out a careful study of a single channel on the southwest flank of Mars' Ascraeus Mons volcano, one of the three clustered volcanoes collectively called the Tharsis Montes. To piece together images covering more than 270 kilometers (~168 miles) of this channel, the team relied on high-resolution pictures from three cameras—the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Context Imager (CTX) and the High/Super Resolution Stereo Color (HRSC) imager—as well as earlier data from the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA). These data gave a much more detailed view of the surface than previously available.
Bleacher and his colleagues carried out a careful study of a single channel on the southwest flank of Mars' Ascraeus Mons volcano, one of the three clustered volcanoes collectively called the Tharsis Montes. To piece together images covering more than 270 kilometers (~168 miles) of this channel, the team relied on high-resolution pictures from three cameras—the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), the Context Imager (CTX) and the High/Super Resolution Stereo Color (HRSC) imager—as well as earlier data from the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA). These data gave a much more detailed view of the surface than previously available.
